Your What is the function of superior mesenteric vein images are available. What is the function of superior mesenteric vein are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the What is the function of superior mesenteric vein files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for what is the function of superior mesenteric vein images information related to the what is the function of superior mesenteric vein interest, you have come to the ideal site. Our website frequently gives you hints for seeking the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more enlightening video articles and images that match your interests.
What Is The Function Of Superior Mesenteric Vein. At its termination behind the neck of the pancreas the superior mesenteric vein combines with the splenic vein to form the hepatic portal vein. The superior mesenteric vein also known as SMV transports blood from the small intestine and the cecum. Moreover less extensive thrombosis is associated with less risk of long-term sequelae of portal venous hypertension. This vein is located in the abdominal cavity next to the superior mesenteric artery.
 Schematic Illustrations Of Superior Mesenteric Vein Smv Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
Schematic Illustrations Of Superior Mesenteric Vein Smv Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
At its termination behind the neck of the pancreas the superior mesenteric vein combines with the splenic vein to form the hepatic portal vein. The superior mesenteric vein also known as SMV transports blood from the small intestine and the cecum. The superior mesenteric artery is the largest of all the aortic branches and carries more than 10 of the cardiac output. The survival of patients who underwent pancreaticoduodenectomy with or without en bloc resection of the superior mesenteric-portal vein SMPV confluence for adenocarcinoma of the pancreatic head was compared. If the artery clogs with plaque or develops a clot blood flow to digestive organs slows. Together the superior and inferior mesenteric veins drain the majority of the gastrointestinal tract from the stomach to the rectum.
The gastrointestinal tract is supplied by the celiac superior mesenteric and inferior mesenteric arteries.
The superior mesenteric vein also known as SMV transports blood from the small intestine and the cecum. -superior mesenteric vein hepatic portal vein liver hepatic veins inferior vena cava heart Which of the following is NOT a direct branch of the aortic arch. If the artery clogs with plaque or develops a clot blood flow to digestive organs slows. To be considered for surgery patients were required to fulfil the following computed tomography criteria for resectability. The superior mesenteric artery plays a vital role in keeping the digestive system healthy and functioning. Just after the superior mesenteric artery passes behind the neck of the pancreas it starts giving off its branches it is always.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
It rotates 180 degrees counterclockwise which places the cecum inferior to the liver and pulls the down the ascending colon. Just after the superior mesenteric artery passes behind the neck of the pancreas it starts giving off its branches it is always. Moreover less extensive thrombosis is associated with less risk of long-term sequelae of portal venous hypertension. At its termination behind the neck of the pancreas the superior mesenteric vein combines with the splenic vein to form the hepatic portal vein. Specifically it drains the small intestine caecum ascending and transverse parts of the colon and distal parts.
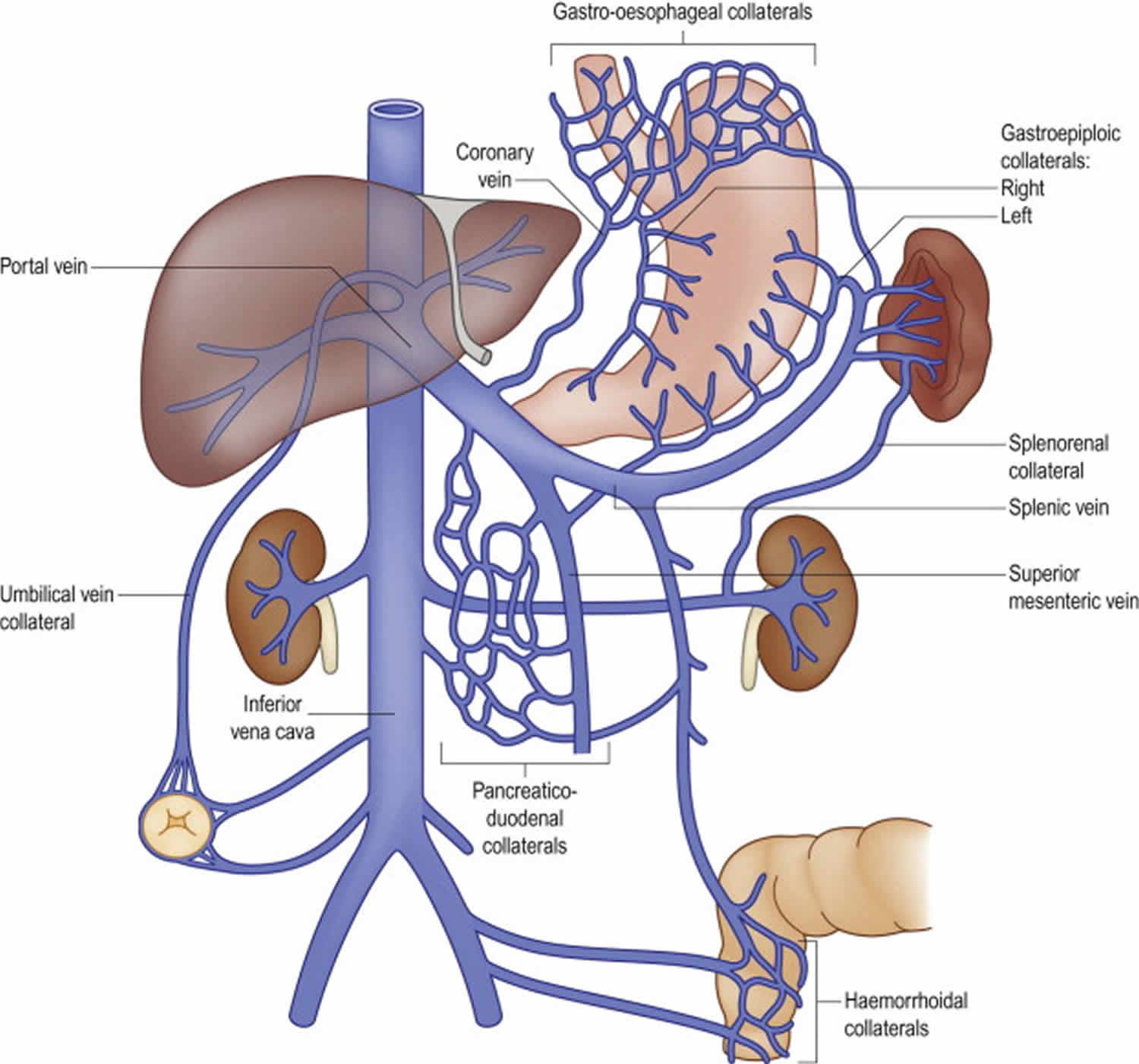 Source: healthjade.net
Source: healthjade.net
It rotates 180 degrees counterclockwise which places the cecum inferior to the liver and pulls the down the ascending colon. Thereby the inferior splenic vein drains blood from the rectum sigmoid descending and distal transverse colon. The main function of the superior mesenteric vein is to drain the blood from the distal portion of the gastrointestinal tract. Inferior mesenteric artery supplies the organs of the hindgut the distal one third of the transverse colon splenic flexure descending colon sigmoid colon and rectum. The superior mesenteric vein is a blood vessel that drains blood from the small intestine jejunum and ileum.
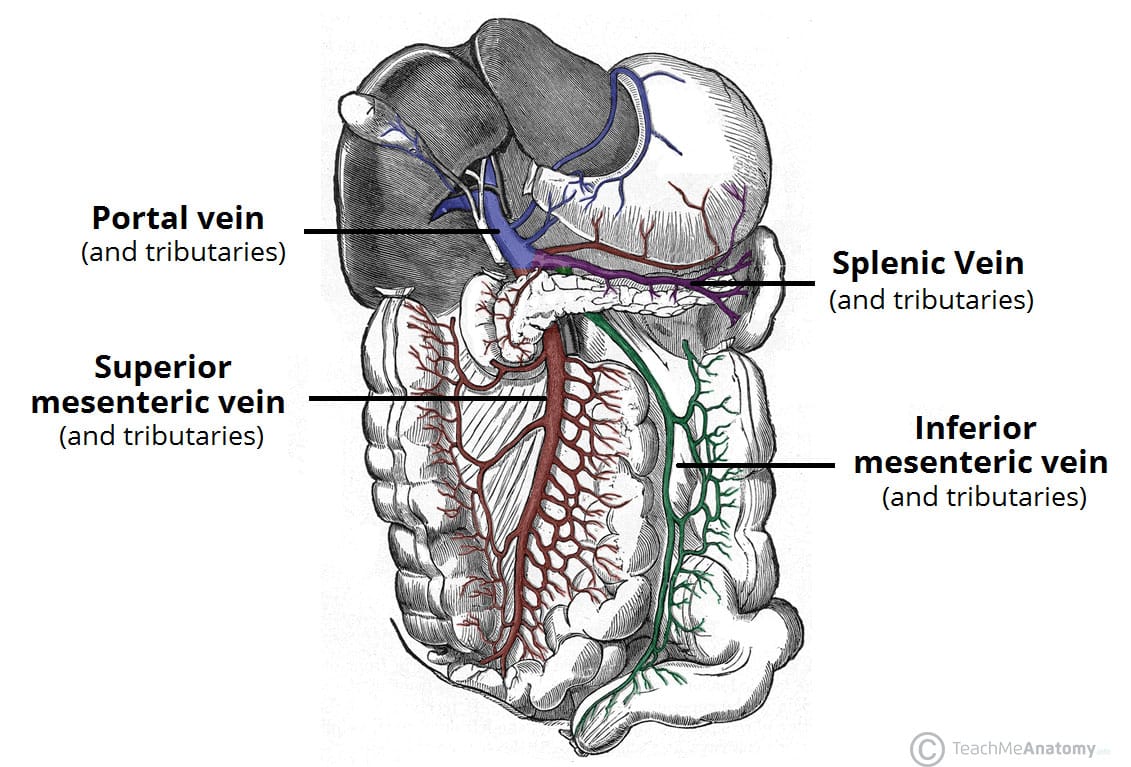 Source: teachmeanatomy.info
Source: teachmeanatomy.info
Patients with thrombosis extending into the portal vein or complete thrombosis of the superior mesenteric vein were also found to have an increased risk of bowel resection. Small mesenteric arteries form an extensive vascular network in the submucosa Figure 12-15. Patients with thrombosis extending into the portal vein or complete thrombosis of the superior mesenteric vein were also found to have an increased risk of bowel resection. This vein is located in the abdominal cavity next to the superior mesenteric artery. Moreover less extensive thrombosis is associated with less risk of long-term sequelae of portal venous hypertension.
-superior mesenteric vein hepatic portal vein liver hepatic veins inferior vena cava heart Which of the following is NOT a direct branch of the aortic arch. This vein is located in the abdominal cavity next to the superior mesenteric artery. The gastrointestinal tract is supplied by the celiac superior mesenteric and inferior mesenteric arteries. The superior mesenteric artery arises from the anterior surface of the aorta just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk and supplies the intestine from the duodenum and pancreas to the left colic flexure. Patients with thrombosis extending into the portal vein or complete thrombosis of the superior mesenteric vein were also found to have an increased risk of bowel resection.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
The two veins that form hepatic portal vein are the splenic vein and the superior mesenteric vein. If the artery clogs with plaque or develops a clot blood flow to digestive organs slows. The superior mesenteric artery is the largest of all the aortic branches and carries more than 10 of the cardiac output. Specifically it drains the small intestine caecum ascending and transverse parts of the colon and distal parts. Patients with thrombosis extending into the portal vein or complete thrombosis of the superior mesenteric vein were also found to have an increased risk of bowel resection.
 Source: mayoclinicproceedings.org
Source: mayoclinicproceedings.org
Inferior mesenteric artery supplies the organs of the hindgut the distal one third of the transverse colon splenic flexure descending colon sigmoid colon and rectum. -superior mesenteric vein hepatic portal vein liver hepatic veins inferior vena cava heart Which of the following is NOT a direct branch of the aortic arch. It follows a path similar to that of the superior mesenteric artery. The superior mesenteric artery is the largest of all the aortic branches and carries more than 10 of the cardiac output. At its termination behind the neck of the pancreas the superior mesenteric vein combines with the splenic vein to form the hepatic portal vein.
 Source: kenhub.com
Source: kenhub.com
Inferior mesenteric artery supplies the organs of the hindgut the distal one third of the transverse colon splenic flexure descending colon sigmoid colon and rectum. Is the ascending and descending colon intraperitoneal retroperitoneal or secondarily retroperitoneal. If the artery clogs with plaque or develops a clot blood flow to digestive organs slows. The superior mesenteric vein SMV is a large blood vessel in the abdomen. The superior mesenteric vein SMV is a major venous tributary of the abdominal cavity.
 Source: kenhub.com
Source: kenhub.com
This large vein receives blood from several other veins tributaries in the digestive tract. Moreover less extensive thrombosis is associated with less risk of long-term sequelae of portal venous hypertension. The gastrointestinal tract is supplied by the celiac superior mesenteric and inferior mesenteric arteries. At its termination behind the neck of the pancreas the superior mesenteric vein combines with the splenic vein to form the hepatic portal vein. Mesenteric vein - definition of mesenteric vein by The Free Dictionary.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
It rotates 180 degrees counterclockwise which places the cecum inferior to the liver and pulls the down the ascending colon. It rotates 180 degrees counterclockwise which places the cecum inferior to the liver and pulls the down the ascending colon. Mesenteric vein - definition of mesenteric vein by The Free Dictionary. Patients with thrombosis extending into the portal vein or complete thrombosis of the superior mesenteric vein were also found to have an increased risk of bowel resection. The superior mesenteric artery arises from the anterior surface of the aorta just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk and supplies the intestine from the duodenum and pancreas to the left colic flexure.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
It follows a path similar to that of the superior mesenteric artery. This large vein receives blood from several other veins tributaries in the digestive tract. The superior mesenteric artery arises from the anterior surface of the aorta just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk and supplies the intestine from the duodenum and pancreas to the left colic flexure. Together the superior and inferior mesenteric veins drain the majority of the gastrointestinal tract from the stomach to the rectum. To be considered for surgery patients were required to fulfil the following computed tomography criteria for resectability.
 Source: kenhub.com
Source: kenhub.com
Embryologically derived in association with the vitelline vein the superior mesenteric vein lies lateral to the superior mesenteric artery SMA and serves to drain the vast majority of the organs of the abdominal cavity. If the artery clogs with plaque or develops a clot blood flow to digestive organs slows. The survival of patients who underwent pancreaticoduodenectomy with or without en bloc resection of the superior mesenteric-portal vein SMPV confluence for adenocarcinoma of the pancreatic head was compared. The main function of the superior mesenteric vein is to drain the blood from the distal portion of the gastrointestinal tract. Is the ascending and descending colon intraperitoneal retroperitoneal or secondarily retroperitoneal.
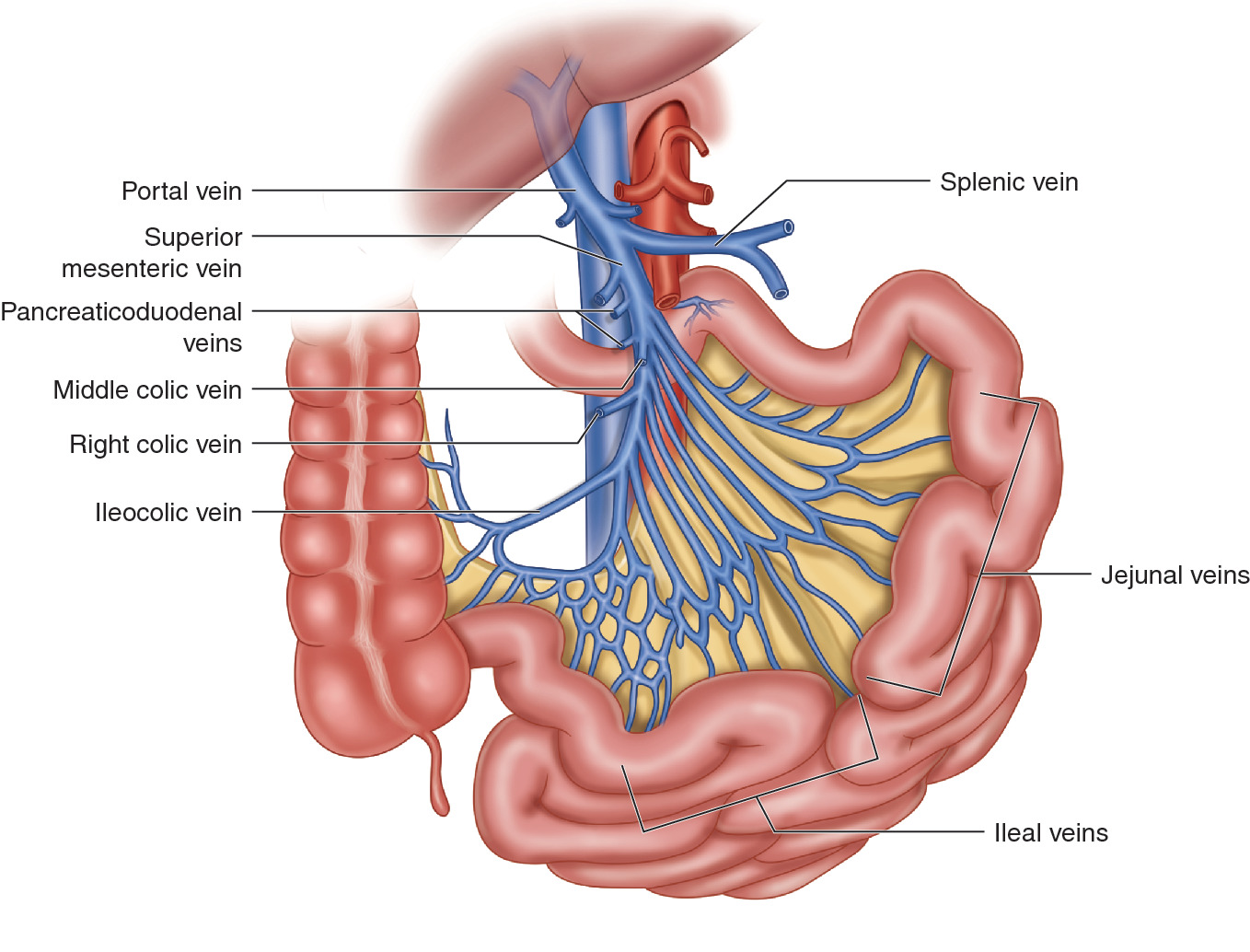 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
Embryologically derived in association with the vitelline vein the superior mesenteric vein lies lateral to the superior mesenteric artery SMA and serves to drain the vast majority of the organs of the abdominal cavity. Moreover less extensive thrombosis is associated with less risk of long-term sequelae of portal venous hypertension. Imaging revealed that they had Wilkies syndrome also known as superior mesenteric artery syndrome which was causing obstruction to a structure that the superior mesenteric artery crosses over. The two veins that form hepatic portal vein are the splenic vein and the superior mesenteric vein. The venous drainage of the mesentery is via the superior mesenteric vein SMV and inferior mesenteric vein IMV which both run alongside their associated arteries.
 Source: kenhub.com
Source: kenhub.com
It arises from the abdominal aorta and supplies arterial blood to the organs of the midgut which spans from the major duodenal papilla of the duodenum to the proximal 23 of the transverse colon. The superior mesenteric artery plays a vital role in keeping the digestive system healthy and functioning. The superior mesenteric vein SMV is a major venous tributary of the abdominal cavity. Is the ascending and descending colon intraperitoneal retroperitoneal or secondarily retroperitoneal. This vein is located in the abdominal cavity next to the superior mesenteric artery.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The gastrointestinal tract is supplied by the celiac superior mesenteric and inferior mesenteric arteries. Inferior mesenteric artery supplies the organs of the hindgut the distal one third of the transverse colon splenic flexure descending colon sigmoid colon and rectum. The venous drainage of the mesentery is via the superior mesenteric vein SMV and inferior mesenteric vein IMV which both run alongside their associated arteries. Specifically it drains the small intestine caecum ascending and transverse parts of the colon and distal parts. The gastrointestinal tract is supplied by the celiac superior mesenteric and inferior mesenteric arteries.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
-superior mesenteric vein hepatic portal vein liver hepatic veins inferior vena cava heart Which of the following is NOT a direct branch of the aortic arch. Rarely the superior mesenteric artery presses against a renal vein or the duodenum causing potentially life-threatening problems. The superior mesenteric artery is the largest of all the aortic branches and carries more than 10 of the cardiac output. It rotates 180 degrees counterclockwise which places the cecum inferior to the liver and pulls the down the ascending colon. The gastrointestinal tract is supplied by the celiac superior mesenteric and inferior mesenteric arteries.

The superior mesenteric vein also known as SMV transports blood from the small intestine and the cecum. This large vein receives blood from several other veins tributaries in the digestive tract. These veins usually receive blood from the. The superior mesenteric artery arises from the anterior surface of the aorta just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk and supplies the intestine from the duodenum and pancreas to the left colic flexure. To be considered for surgery patients were required to fulfil the following computed tomography criteria for resectability.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
These veins usually receive blood from the. Inferior mesenteric artery supplies the organs of the hindgut the distal one third of the transverse colon splenic flexure descending colon sigmoid colon and rectum. Together the superior and inferior mesenteric veins drain the majority of the gastrointestinal tract from the stomach to the rectum. A 20-year-old patient who was misdiagnosed with an eating disorder returned to their physician with persisting abdominal pain and intermittent vomiting. Is the ascending and descending colon intraperitoneal retroperitoneal or secondarily retroperitoneal.
 Source: teachmeanatomy.info
Source: teachmeanatomy.info
It follows a path similar to that of the superior mesenteric artery. The venous drainage of the mesentery is via the superior mesenteric vein SMV and inferior mesenteric vein IMV which both run alongside their associated arteries. At its termination behind the neck of the pancreas the superior mesenteric vein combines with the splenic vein to form the hepatic portal vein. The superior mesenteric vein also known as SMV transports blood from the small intestine and the cecum. Is the ascending and descending colon intraperitoneal retroperitoneal or secondarily retroperitoneal.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title what is the function of superior mesenteric vein by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






